DestinE in motion: key progress from ECMWF, ESA and EUMETSAT

Launched in 2022, Destination Earth (DestinE) is set out to build a twin – or replica – of our planet based on cutting-edge science and supercomputing capabilities. The digital twins representing different aspects of the Earth system will provide scientists, businesses and policymakers insights about the past, present and possible future scenarios of the impacts of climate change and extreme events.
While the full ecosystem is maturing, a lot has already been achieved by the organisations chosen by the European Commission to bring this ambitious vision to life: ECMWF, ESA, and EUMETSAT together with many institutions across Europe.
ECMWFEuropean Centre for Medium-Range Weather Forecasts More – developing the Digital Twins
ECMWFEuropean Centre for Medium-Range Weather Forecasts More is working on DestinE’s Digital Twins and has made great progress since the beginning of the initiative.
The Climate Change Adaptation Digital Twin and the Weather-induced Extremes Digital Twin now produce global high-resolution simulations of extreme weather events, climate projections and ‘what-if’ climate scenarios. They provide insights to sectors most impacted by climate change and weather extremes.
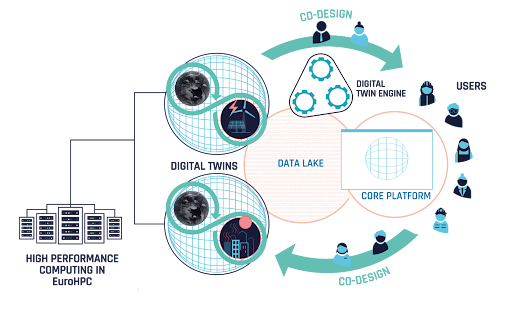
DestinE’s components and their interaction with each other and the High-Performance Computing provided by EuroHPC JU
Together with a hundred partner institutions across Europe, ECMWFEuropean Centre for Medium-Range Weather Forecasts More has built and demonstrated the capabilities of the digital twins and the underlying software infrastructure – the Digital Twin Engine. This infrastructure enables the seamless operation of the digital twins and handling in the distributed DestinE ecosystem.
Cutting-edge Earth system simulations are now regularly produced, leveraging the supercomputing facilities of the European High-Performance Computing Joint Undertaking (EuroHPC JU). Distributed across Europe, these supercomputers are key to DestinE and provide the computing power needed to operate the digital twins. DestinE is the world’s first large-scale effort to develop Earth system digital twin technology, and the strategic partnership with EuroHPC JU is a key enabler for the task.
ECMWFEuropean Centre for Medium-Range Weather Forecasts More is also implementing advanced artificial intelligence and machine learning (AI/ML) techniques in order to boost the Digital Twins and Digital Twin Engine’s capabilities.
ESAEuropean Space Agency – opening the DestinE PlatformSelf-standing DestinE system component, interfacing with the More
ESAEuropean Space Agency is responsible for developing and implementing the DestinE Platform – the main entry point for all DestinE users.
The platform brings together and operates a wide ecosystem of services within an open and secure cloud environment. Some of these services provide access to data from not only DestinE’s Digital Twins, but also a variety of other sources. Users can process, manipulate and visualise data, while also benefiting from a flexible and freely accessible suite of tools, as well as new insights.

The DestinE PlatformSelf-standing DestinE system component, interfacing with the More
Originally, full access to the platform and its services was restricted to specific users but it is now open to larger groups. Users are welcome to register, access the platform and explore the 23 services currently available. The ultimate aim is to meet the needs of a broad and diverse community, including the general public, scientists, commercial organisations and policymakers.
While a lot of Earth observation (EO) data has been freely available across Europe and beyond for decades through initiatives like Copernicus, the DestinE PlatformSelf-standing DestinE system component, interfacing with the More takes this a step further. It makes powerful services and applications more accessible, not just to Earth observation experts, but also to users who may not have technical knowledge, yet can benefit from EO-driven insights for their work or areas of interest.
EUMETSATEuropean Organisation for the Exploitation of Meteorological – new data bridges and releases
EUMETSAT’s contribution to DestinE focuses on the Data Lake component.
The Data Lake stores data produced by DestinE’s Digital Twins and provides access to volumes of information from ECMWFEuropean Centre for Medium-Range Weather Forecasts More, ESAEuropean Space Agency and EUMETSATEuropean Organisation for the Exploitation of Meteorological. It also offers Big Data processing services to work efficiently with DestinE data.
A recent achievement by EUMETSATEuropean Organisation for the Exploitation of Meteorological relates to the underlying infrastructure of DestinE, particularly the data bridges. These hardware and software components are crucial elements in the DestinE architecture that connect multiple data sources and processing services. They make it possible for users to connect to datasets regardless of where the data is located, and thus support them in the process of creating services and new applications.
EUMETSAT’s latest data bridges have been deployed in two locations: one near the MareNostrum supercomputer in Spain, and the other close to EUMETSAT’s own data store in Germany. Both bridges improve data access and performance by bringing processing capabilities closer to the source.
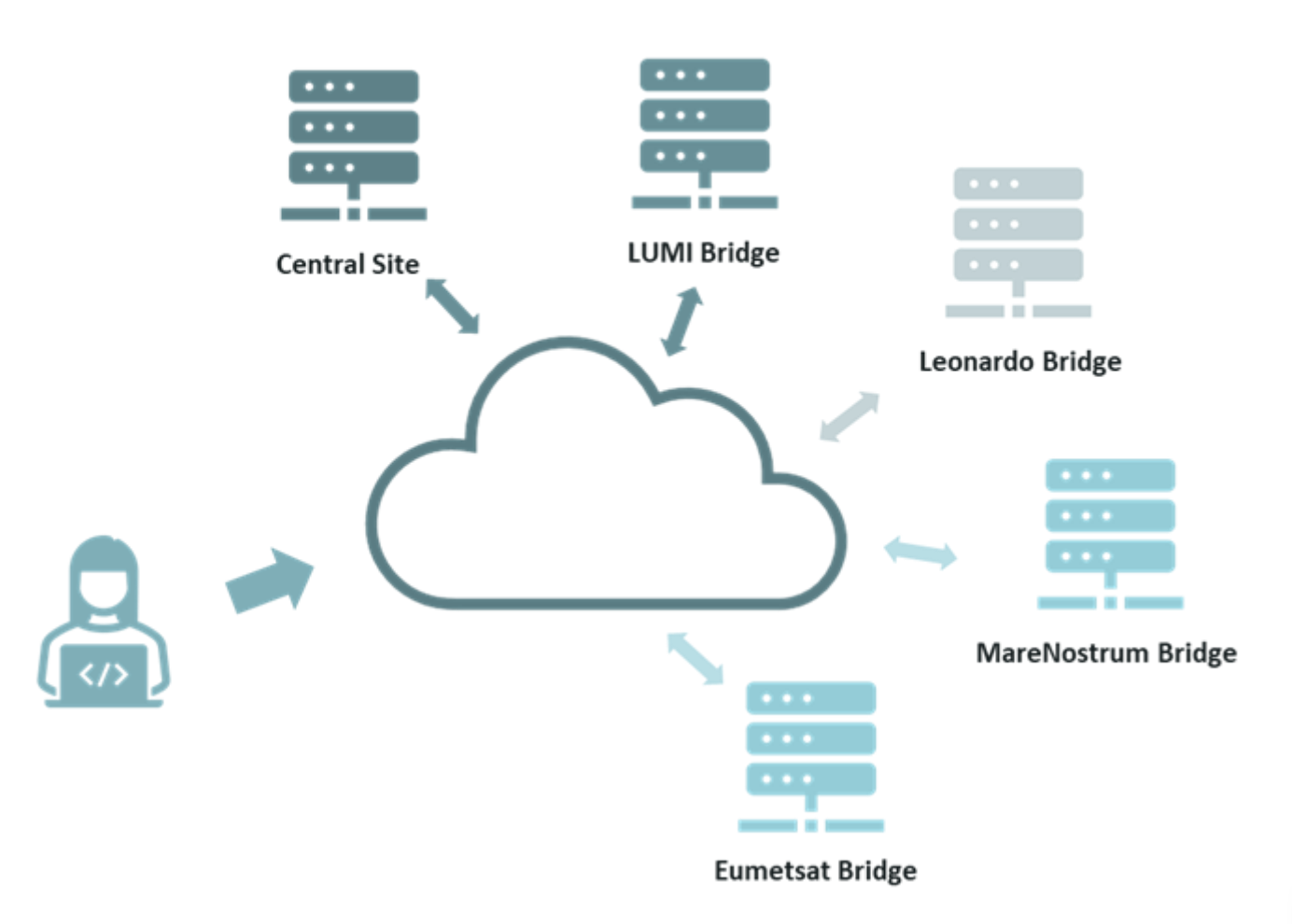
Data bridges within the Data Lake architecture
In addition, EUMETSATEuropean Organisation for the Exploitation of Meteorological has recently made the DestinE EDGE services available to all DestinE users. These services – STACKA DestinE Data Lake Edge Service providing hosted applicatio, ISLET, and HOOKA DestinE Data Lake Edge service providing high-level pre-de – take advantage of the data bridges. When users access them, they are directly connected to a data bridge relevant to the data they are exploring. This direct connection enables faster access and a more efficient application development process. Ultimately, these tools support faster data processing and thereby strengthen the DestinE ecosystem.
As the DestinE ecosystem continues to grow, further updates will be shared through the DestinE website and at various events and sessions – including the 4th DestinE User eXchange happening this week in Austria. To stay up to date with the latest developments, subscribe to the DestinE newsletter!